+1-888-201-6088 | email@nevronoffice.com
Work with Automatic Layout in Nevron DrawNevron Draw comes with the most important automatic layouts readily made for you to apply with just one click. To see the power of the automatic layouts, begin by adding a number of shapes to a new document and connecting them, and then navigate to the “Arrange Tab”, where you’ll see the “Layout Shapes” function.
Currently, the available preset layouts are:
Here are some examples of the various layouts and what they’re suitable for:s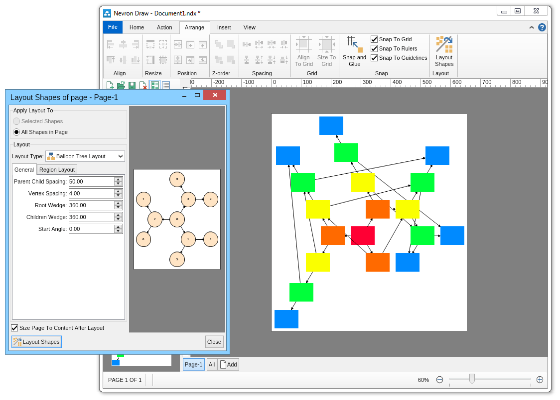 Balloon tree automatic layoutThe balloon tree layout tries to compact the drawing area of the diagram by placing the vertices in balloons around the tree root. It produces straight line tree drawings.There are multiple aspects of the balloon tree automatic layout that you can control, including:
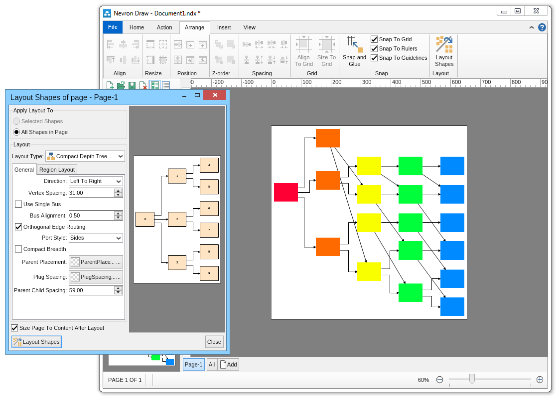 Compact depth tree automatic layoutThe compact depth tree layout is a classical directed tree layout, which tries to compact the depth of the drawing area.This layout is very useful when arranging deep, unbalanced trees with different node sizes (class diagrams being a perfect example). In cases like these the layout guarantees that the drawing is with minimal depth.  Layered graph automatic layoutThe Layered Graph Layout is a hierarchical graph layout, used to layout a graph in layers. The layout distributes the graph vertices to layers, then it tries to minimize the edge crossings on a layer by layer basis. Finally the layout performs the breadth vertex placement and edge routing step. Supports both polyline and orthogonal edge routings.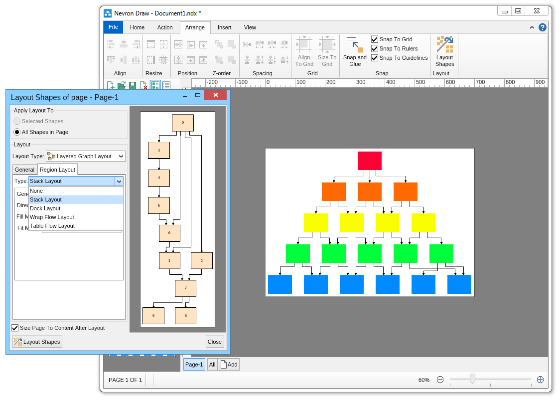 Layered graph stack automatic layoutThis layout is simply a variation of the layered graph automatic layout, achieved by modifying the type of the region layout.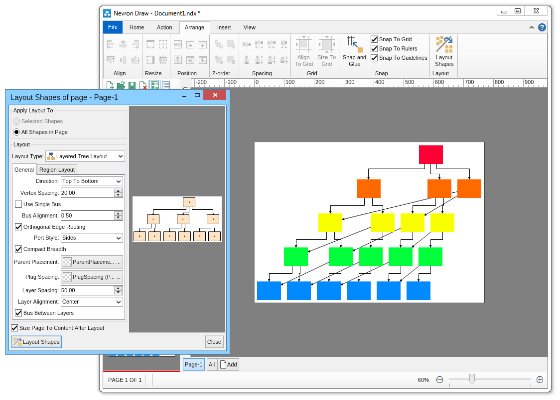 Layered tree automatic layoutThe layered tree layout represents a classical directed tree layout (e.g. with uniform parent placement), which places shapes from the same level in layers. It produces both straight line and orthogonal tree drawings.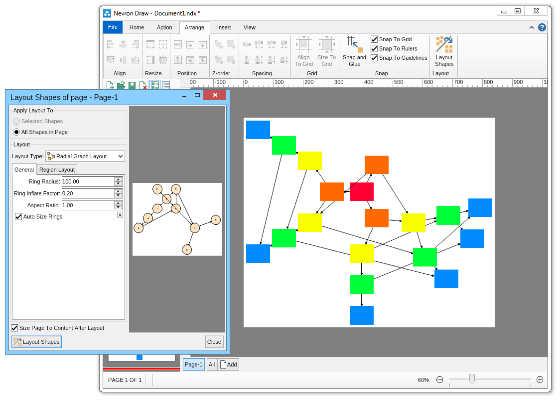 Radial graph automatic layoutThe Radial Graph Layout, layouts the graphs in concentric circles. The shapes with no predecessors are placed in the center and their descendants are placed on the next circle and so on. It produces a straight line graph drawing.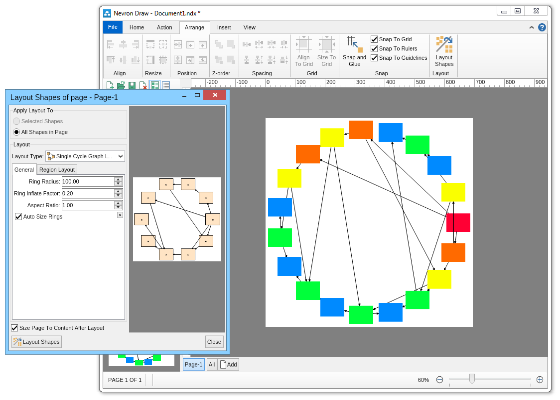 Single cycle automatic layoutThe single cycle layout layouts all graph shapes on a single circle, trying to minimize the number of edge crossings.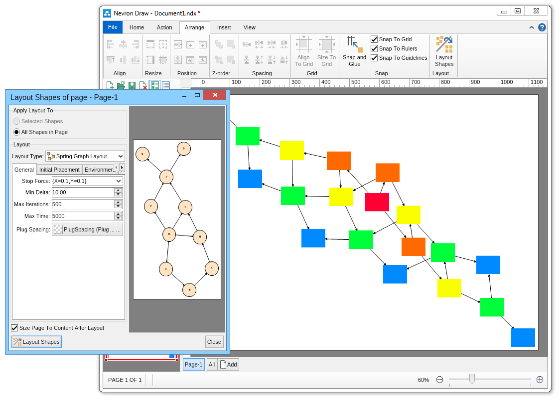 Spring graph automatic layoutThe Spring Graph Layout is a classical force directed layout, which uses a spring and electrical forces. The spring force tries to enforce a certain distance between connected shapes. The electrical force repels the shapes which are close to each other. Nevron Diagram Spring Graph Layout provides numerous tuning options.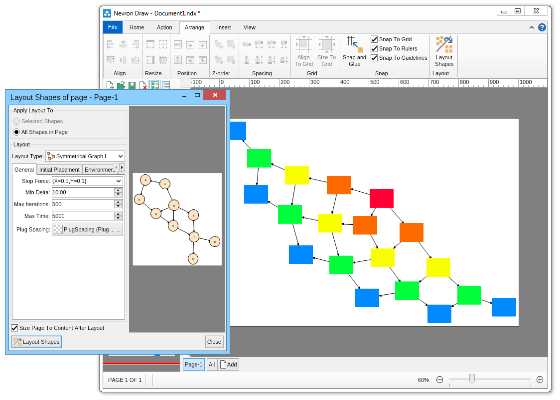 Symmetrical graph automatic layoutThe symmetrical layout represents an implementation of the Fruchertman and Reingold force directed layout (with some modifications). It uses attractive and repulsive forces, which aim to produce a drawing with uniform distance between each set of connected shapes. Because of that the drawing tends to be symmetrical. |
We use cookies to allow us to automate the access and the data entry functions of our website and to correlate online ordering information for purchases you may make while at the website (if any), tailor our website to your preferences or interests, or customize promotions or marketing. For full details read our cookie policy.